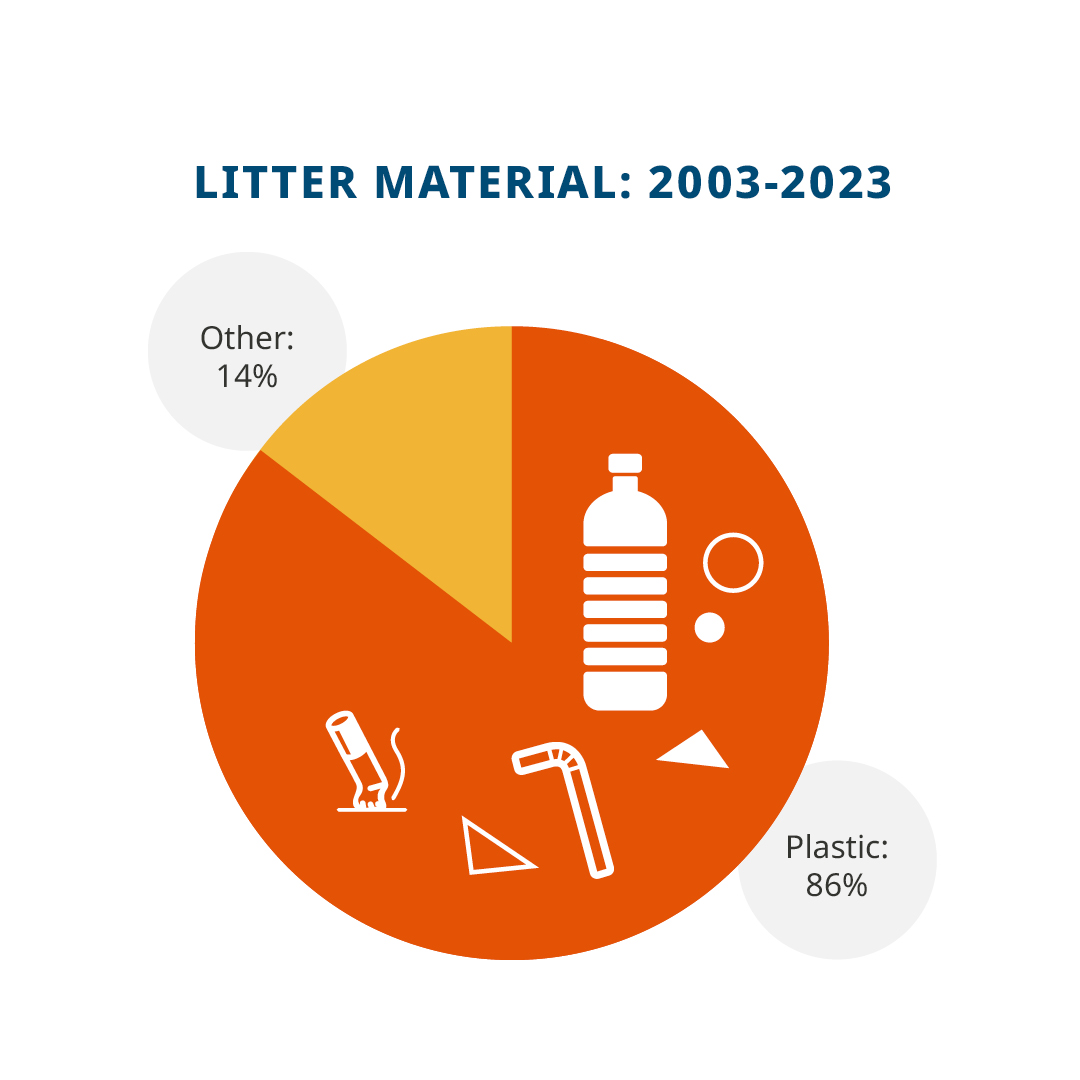
CHICAGO, IL (April 11, 2024) – Eighty six percent of litter collected on Great Lakes beaches is composed either partially or fully of plastic, according to a new report released by the Alliance for the Great Lakes. The report is based on 20 years of data collected from more than 14,000 Adopt-a-Beach cleanups on all five Great Lakes. The new analysis details the most common types of plastic items found on Great Lakes shorelines and outlines potential solutions to reduce plastic pollution. In the environment, plastics never go away. Instead, they break down into toxic microplastic particles that make their way into the Great Lakes, a source of drinking water for 40 million people.
Plastic pollution threatens human health & the environment
“Plastic pollution in the Great Lakes is a threat to both human health and the environment,” said Olivia Reda, the author of the report and the Volunteer Engagement Manager at the Alliance for the Great Lakes. “The volume of plastic found on our shorelines demonstrates the urgent need to pass federal, state, and local laws that reduce plastic pollution getting into the lakes. While our dedicated volunteers are cleaning up literally tons of litter each year, more of this plastic litter enters our waters, where it breaks down into tiny particles that are found in our drinking water.”
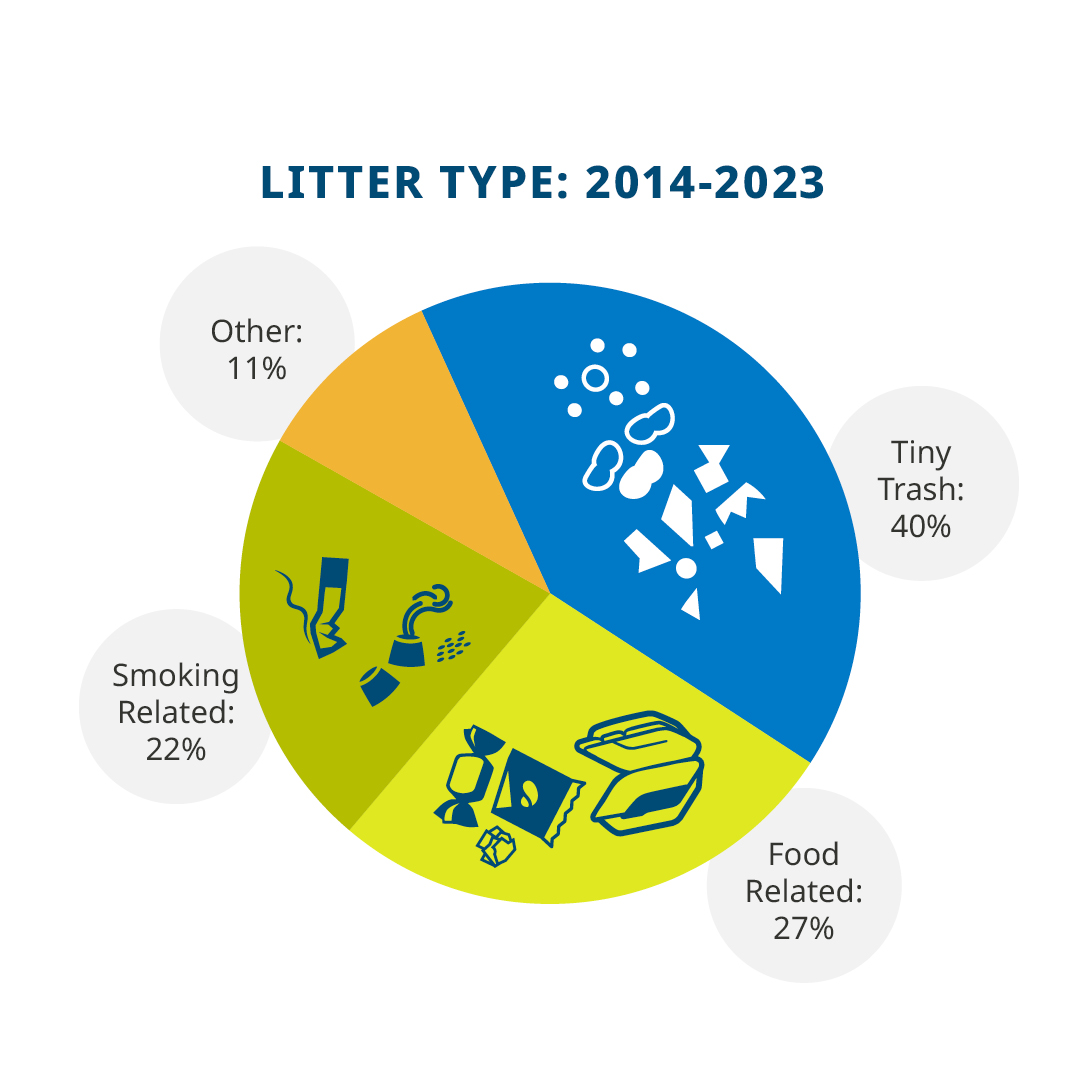
The data in the report, Adopt-a-Beach: 20 Years of Great Lakes Litter Data, reveals alarming and consistent patterns. Most of the litter is plastic, and many are single-use items – used once and left behind – which contain plastic. Volunteers categorize each piece of litter into a type, such as cigarette butts, plastic beverage bottles, or “tiny trash” including plastic pieces, foam pieces, and glass pieces measuring 2.5 cm or less. For the last 10 years, the top litter items collected are tiny plastic pieces, followed by cigarette butts, tiny foam pieces, plastic bottle caps, and food wrappers. Forty percent of all litter is in the “tiny trash” category.
Solutions require action beyond individual behavior change
While it’s important for individuals to reduce their plastic use, the report notes that substantially reducing plastic pollution will require action from businesses, governments, and manufacturers. The Alliance for the Great Lakes is calling for implementing Extended Producer Responsibility policies — holding producers responsible across the life cycle of their products and packaging from design and materials to end-of-life management. Such policies have been in place for years in Europe and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. More recently California, Colorado, Maine, and Oregon have passed versions of these common-sense solutions, which are now being considered across the Great Lakes basin.
Shorter-term solutions include reducing or eliminating the most problematic plastics like single-use bags and foam, deploying new technologies such as microfilters in washing machines to remove plastic microfibers before they enter our water systems, stopping the spills of industrial plastic pellets in the Great Lakes, and increasing access to water refilling stations as well as reuse and refill packaging. These types of policy solutions are moving forward in several Great Lakes states.
The power of citizen science

Since launching in 1991, the Alliance’s Adopt-a-Beach cleanups have evolved into the most extensive volunteer program ever to collect data on Great Lakes beach litter. Volunteers receive training and resources to host year-round cleanups in communities in all eight Great Lakes states. Since the start of the program, over 200,000 volunteers have participated in cleanups, removing over 9,700,000 individual pieces and over 535,000 pounds of litter from the shoreline. In 2003, Adopt-a-Beach launched an online database, which is now the largest litter dataset exclusively for the Great Lakes. The data is available publicly and has been used by educators, community advocates, policy makers, and academic researchers.
“This dataset demonstrates the power of citizen science, when members of the public come together to collect datasets far larger than any single researcher could build,” said Reda. “We are so thankful to the hundreds of thousands of volunteers and supporters who participated in Adopt-a-Beach cleanups over the years. They are environmental heroes committed to reducing litter in their communities and are collecting one-of-a-kind data that will continue shining a light on plastic pollution.”
Read the Report
Download the Executive Summary
If you would like to join the efforts, sign up for an Adopt-a-Beach cleanup. Learn more about plastic pollution here.
###
Contact: Don Carr, Media Director, dcarr@greatlakes.org

